Description
Smart Irrigation System Using IoT
Introduction
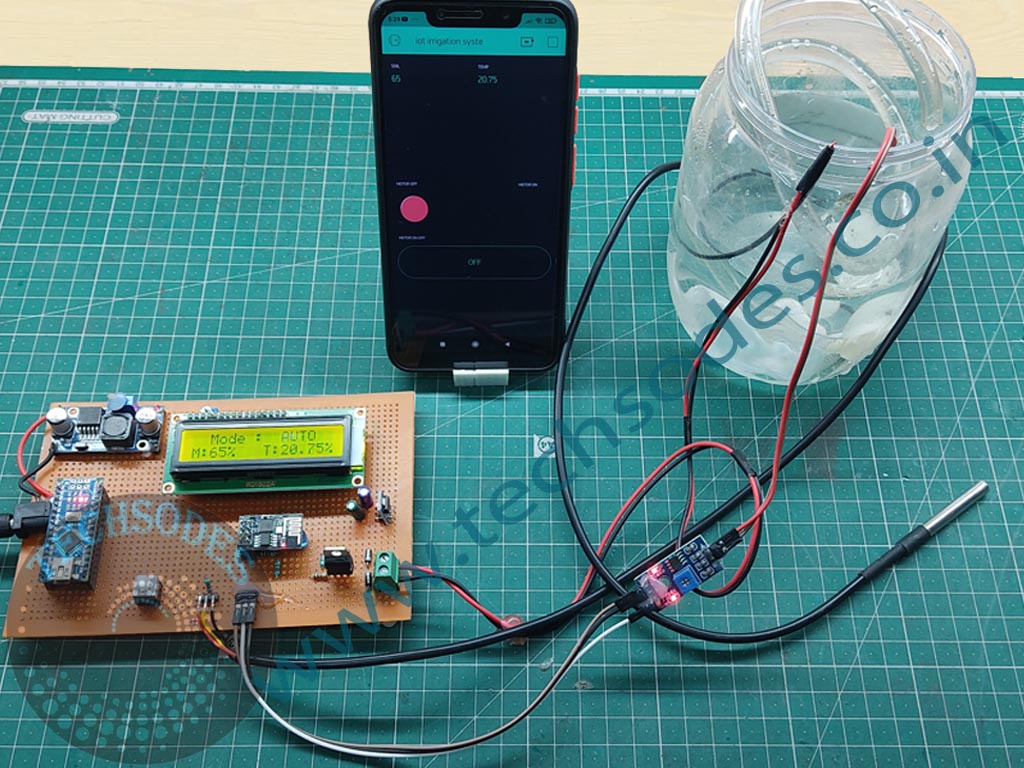
As the global demand for water conservation grows and the need for more efficient farming practices becomes critical, smart irrigation systems have emerged as a solution for modern agriculture. The “Smart Irrigation System Using IoT” is an innovative project designed to automate the watering process based on real-time soil moisture and temperature data. This system utilizes components such as the Arduino Nano, LCD16x2, soil moisture sensor, DS1820 temperature sensor, LM2576 voltage regulator module, and ESP01 Wi-Fi module. A key feature of this project is the incorporation of two operational modes: Manual Mode and Automatic Mode, which give users flexibility in controlling the irrigation process.
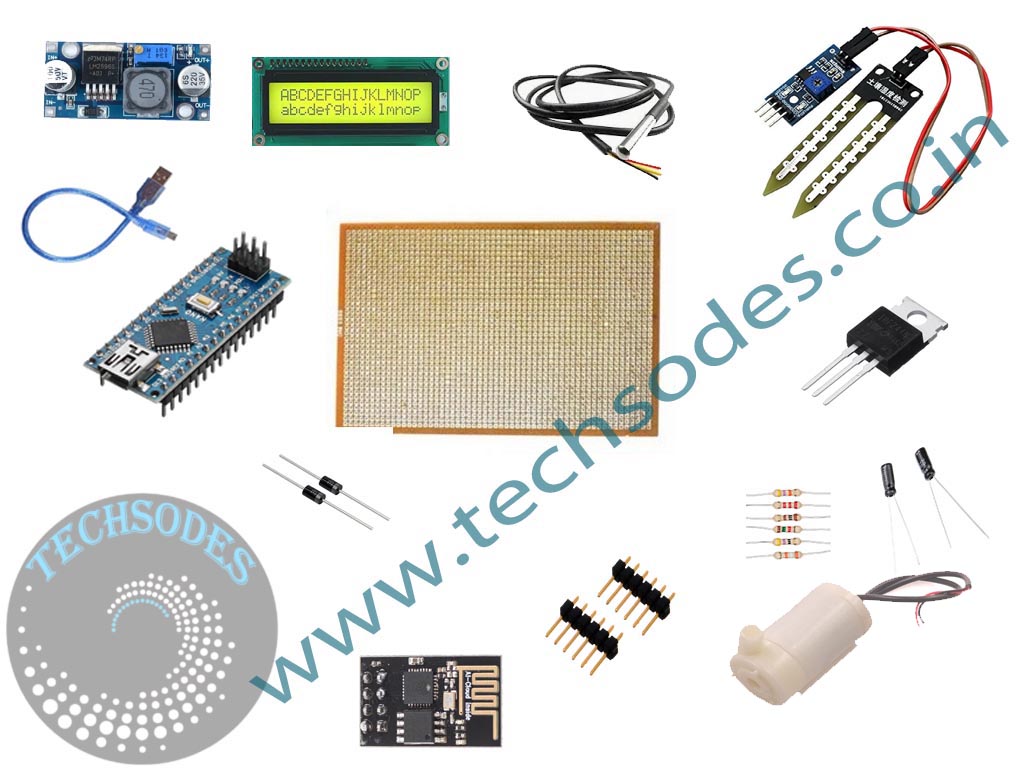
System Components
- Arduino Nano: This microcontroller is the heart of the system. It processes data from the sensors and manages both manual and automatic irrigation modes.
- LCD16x2: The LCD16x2 display is used to show real-time information, including the moisture level, temperature, system status, and the current operational mode (Manual or Automatic).
- Soil Moisture Sensor: This sensor measures the moisture content in the soil. In automatic mode, if the soil is too dry, the system automatically triggers the irrigation process.
- DS1820 Temperature Sensor: The DS1820 monitors the ambient temperature, which plays an important role in water management. Higher temperatures may cause faster evaporation, influencing the irrigation decision.
- LM2576 Voltage Regulator Module: This module ensures a stable power supply for the various components by stepping down the voltage to suitable levels for the Arduino and other connected parts.
- ESP01 Wi-Fi Module: The ESP01 Wi-Fi module connects the system to the internet, enabling remote monitoring and control. The user can switch between manual and automatic modes and manage irrigation via a smartphone or web application.
- Water Pump: The pump is responsible for irrigating the field when the system detects low soil moisture levels or when manually triggered by the user.
Working Principle
The Smart Irrigation System operates in two modes: Manual Mode and Automatic Mode. These modes are designed to provide flexibility, allowing the user to either rely on automation or take control of the irrigation process based on personal judgment.
Automatic Mode
In Automatic Mode, the system uses data from the soil moisture sensor and temperature sensor to make real-time irrigation decisions. The Arduino Nano continuously monitors the soil moisture level and compares it with a predefined threshold. If the soil moisture falls below the threshold, the water pump is activated to irrigate the field until the desired moisture level is achieved. This mode is ideal for users who want a fully automated process that optimizes water usage.
In addition to soil moisture, the DS1820 temperature sensor helps determine the irrigation cycle. For example, if the temperature is too high, the system may allow more frequent watering to compensate for increased evaporation. This further enhances the efficiency of the system, ensuring that crops receive adequate water during hot conditions.
Manual Mode
In Manual Mode, the system allows the user to take control of the irrigation process. Using the ESP01 Wi-Fi module, the user can remotely monitor soil moisture and temperature data and manually start or stop the water pump through a smartphone app or web interface. This mode is especially useful when the user wants to intervene in specific situations, such as when weather forecasts predict rain or when crops require special watering schedules.
The mode selection (manual or automatic) is displayed on the LCD16x2, making it easy for the user to know the current operational status. Additionally, the user can switch between the two modes via a button press or through the IoT interface.
System Flow
- Initialization: When the system is powered on, the Arduino Nano initializes the sensors, modules, and display. The current mode (manual or automatic) is displayed on the LCD16x2.
- Mode Selection: The system checks which mode is active. If the system is in automatic mode, it uses sensor data to control irrigation. In manual mode, the user takes direct control.
- Automatic Mode Operation: In automatic mode, the Arduino Nano reads the soil moisture sensor data. If the soil is dry, it activates the pump to irrigate the field. The system continuously updates the LCD16x2 with real-time soil moisture and temperature data.
- Manual Mode Operation: In manual mode, the system awaits user input via the IoT interface. The user can remotely activate or deactivate the water pump through a smartphone or web app. Real-time data is also available for monitoring.
- Remote Access via IoT: The ESP01 module enables the system to be connected to the internet, allowing users to monitor data and control irrigation remotely from anywhere.
- Data Display: The LCD16x2 shows the current soil moisture, temperature, and mode status (manual or automatic).
Benefits of Manual and Automatic Modes
- Flexibility: The dual-mode system provides users with flexibility in controlling irrigation. Automatic mode saves time and labor, while manual mode allows for more precise control when needed.
- Water Conservation: In automatic mode, the system optimizes water usage by irrigating only when necessary. Manual mode allows users to control irrigation based on weather predictions or other conditions.
- Convenience: With the IoT functionality, users can switch between modes and control irrigation remotely from their smartphones, ensuring convenience and ease of use.
- Increased Crop Yield: By providing the right amount of water at the right time, the system helps improve crop yield and health.
- Cost-Effective: The system is built using affordable components like Arduino Nano and ESP01, making it accessible to small-scale farmers.
Conclusion
The “Smart Irrigation System Using IoT” with both manual and automatic modes offers a comprehensive solution for modern agricultural challenges. The automatic mode ensures that crops are watered efficiently based on real-time soil moisture and temperature data, while manual mode allows farmers to take direct control of the irrigation process when needed. This flexible approach to irrigation not only conserves water but also increases productivity and crop health. By integrating IoT, this system provides the added advantage of remote monitoring and control, making it a smart, convenient, and sustainable solution for today’s farming needs.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.